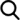A good understanding of the extrusion process is necessary to solve extrusion problems efficiently. It is recommended for the reader new to extrusion to take classes covering the material characteristics of plastics, typical features of extrusion machinery, instrumentation and operating controls, the inner workings of extruders, and screw and die design. Classes and continuing education short courses on extrusion are available from a variety of colleges and organizations. There are also a number of training programs available as videos, interactive computer- based instruction, and web-based instruction. In many extrusion operations, the primary mode of training is on-the-job training. However, on-the-job training is often the least effective and most expensive method of training. Extruders are expensive machines that must be operated correctly to produce good parts. If an extruder is not operated correctly, out-of-spec parts may be produced, or the extruder may be damaged. It is also important to realize that extruders are potentially dangerous devices. Serious accidents can occur when
extruders are not operating properly. Therefore, it is imperative that people who operate extrusion equipment receive comprehensive safety training. A short review of the extrusion process implies the understanding of the functional zones. The functional zones of a conventional single-screw extruder are shown in Figure 1:
- Feed hopper, this zone is designed to operate under gravity flow and it feeds the granules or the particulate solids into the extruder,
- Solids conveying zone, this zone is designed to transport and to slightly compress the granules or the particulate solids
-Plasticating zone, polymer melting takes place in this zone due to viscous dissipation and heat transfer by conduction from the extruder barrel,
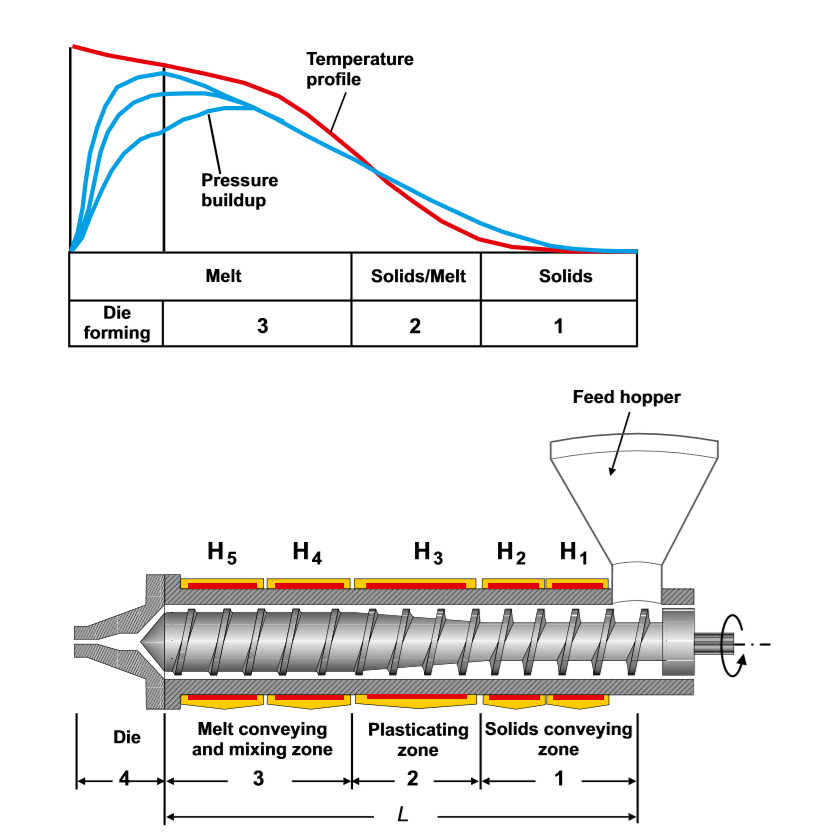
- Melt conveying zone (or metering zone), this zone is intended to transport the molten polymeric material and to achieve pressure buildup,
-Mixing zone, this zone is designed to improve melt homogeneity by means of shear mixing elements, such as distributive, dispersive, or elongational mixers,
- Die forming, the forming or shaping of the extrudate takes place in this zone for subsequent post-extrusion processes, such as calibration, cooling, winding or cutting, among others, and
- Venting, this zone is only present in two-stage screw extruders or vented extruders and is used to remove any residual moisture or volatiles from the polymer melt